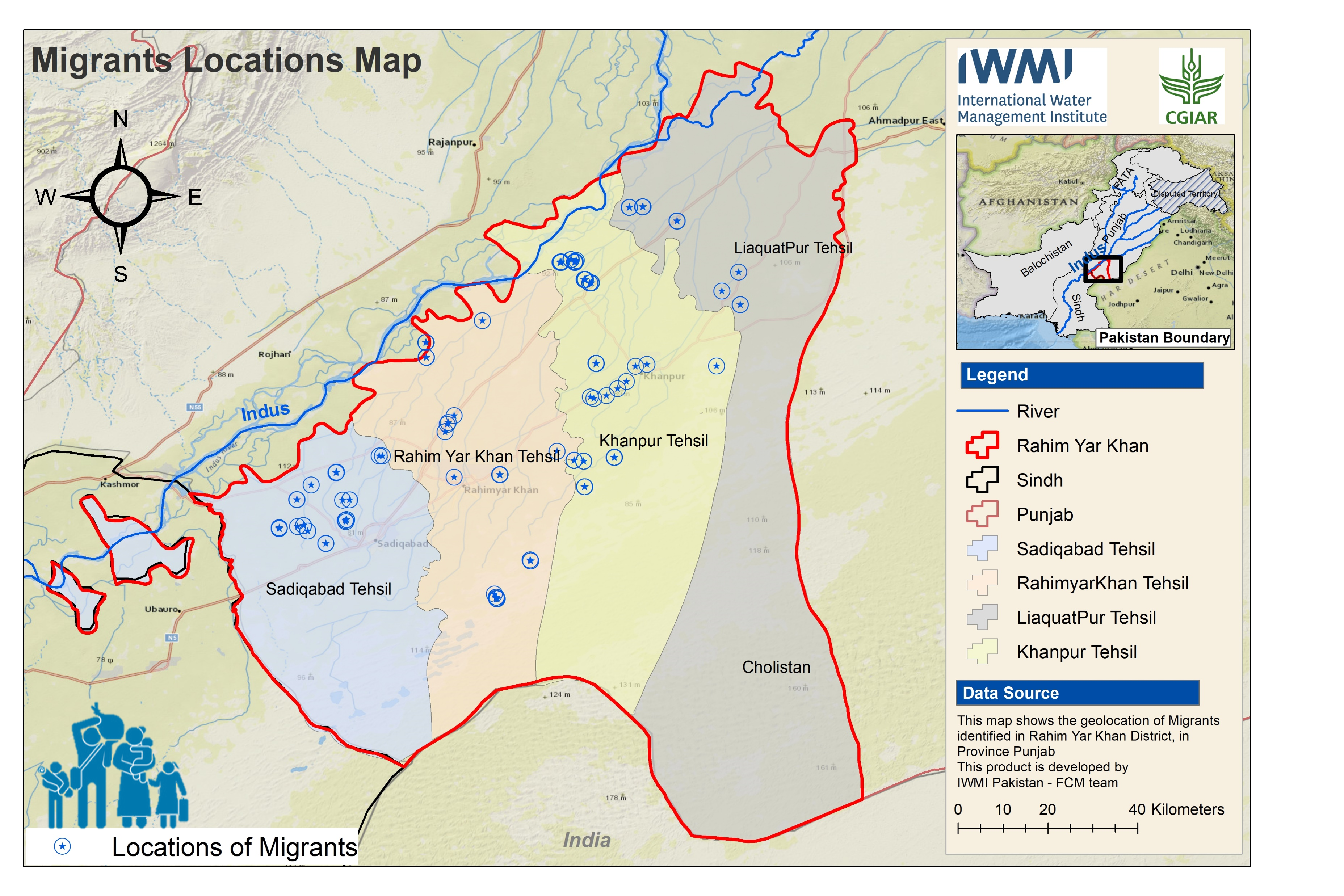
A new curriculum has been developed by researchers of Resource Recovery and Reuse (RRR) at IWMI and business development experts at CEWAS (coaching entrepreneurs in water and sanitation). This curriculum was developed with an aim to transfer knowledge on business development in RRR to graduate students enabling them to analyse business options and enter the RRR market as entrepreneurs. The modules draw on innovative business model examples from the IWMI publication Resource Recovery from Waste Business Models for Energy, Nutrient and Water Reuse in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. An introduction to the curriculum for professors and lecturers was organized at the University of Dar Es Salaam, Tanzania.
A one-and-half day workshop for professors and lecturers from the College of Engineering and Technology – Water Resources Engineering Department was organized on between 8 – 9 April at University of Dar Es Salaam. The lectures were convened by Dr. Miriam Otoo (Research Group Leader and Senior Economist at IWMI) and Dr. Charles B. Niwagaba (Associate Professor at Makerere University), with the support of Dr. Joel Nobert (Head of the Department, Water Resources Management, University of Dar es Salaam) and Dr. Kimwaga (Senior Lecture at the College of Engineering and Technology – Water Resources Engineering Department, University of Dar es Salaam).

The lectures aimed to provide an exposure to the modules of the curriculum. The curriculum is targeted to MSc-level environmental/sanitary engineering /natural sciences/ business students. The university curriculum will enable engineering, business and agriculture students to:
- identify business opportunities for resource recovery and reuse across the waste and sanitation sectors,
- develop RRR business models,
- study the feasibility of RRR business models by analyzing legal, institutional,
- technological, logistical, health and financial aspects and related risks,
- define strategic positioning, financing and action plans for the implementation of RRR business models.
The curriculum consists of:
- three modules on introduction of the course concept, the importance of market-based RRR solutions, business models with a direct link to the feasibility assessment as the underlying methodologies of the course concept;
- four modules on RRR markets (for different resource streams and products/services), analyzing market characteristics and the legal and regulatory framework conditions;
- three modules on technical solutions that can be used for RRR related business models and the safety and health implications and;
- six modules on key business aspects of market positioning, financial planning, financing options, risk management and strategic planning.
Lecturers/professors can either choose to use the modules as stand-alone lectures or use them in the proposed sequence as part of a comprehensive RRR semester course depending on its suitability.